页面置换算法 2020年的CMU15-445 的 Lab1 需要实现 LRU 算法。
2022年的CMU15-445 的 Lab1 需要实现 LRU-K 算法。
LRU
LRU是 Least Recently Used 的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。该算法赋予每个页面一个访问字段,用来记录一个页面自上次被访问以来所经历的时间 t,当须淘汰一个页面时,选择现有页面中其 t 值最大的,即最近最少使用的页面予以淘汰。
实现思路 LRU 的定义相当简单,实现时,只需要维护一个列表来记录最近使用的页面的顺序。
对于这个列表,需要能够用常数级别的时间复杂度将列表中的一个元素移动到列表一边 (最近使用顺序的更新)。
双端链表在知道节点指针是删除一个元素的时间复杂度为 O(1), 节点指针可以通过哈希映射的方式快速获得。
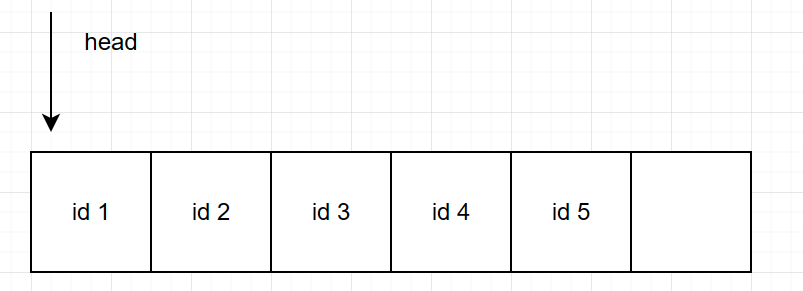
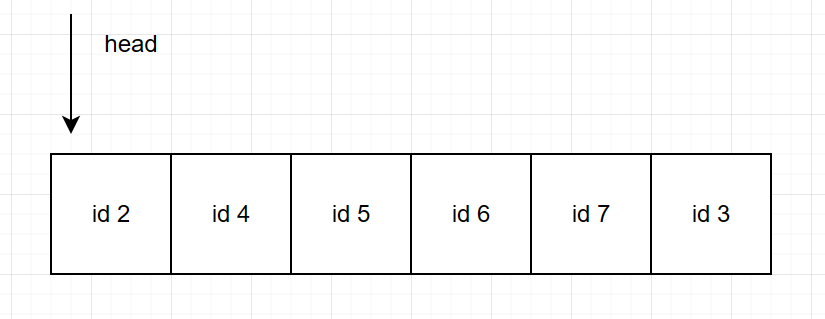
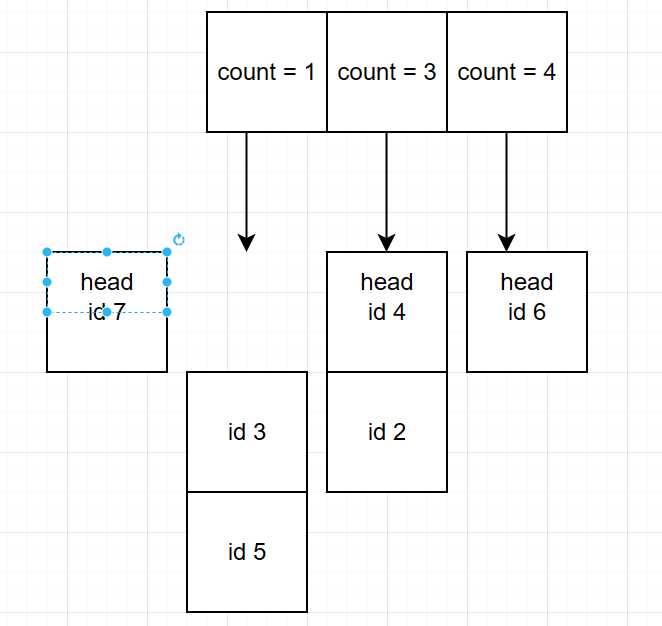
假设内存可以容纳 6 个页,按照 1,2,3,4,5 的顺序访问,双端链表是这样记录的:
head 就是访问时间最早的, 如果容量满了,就要取出 head 。
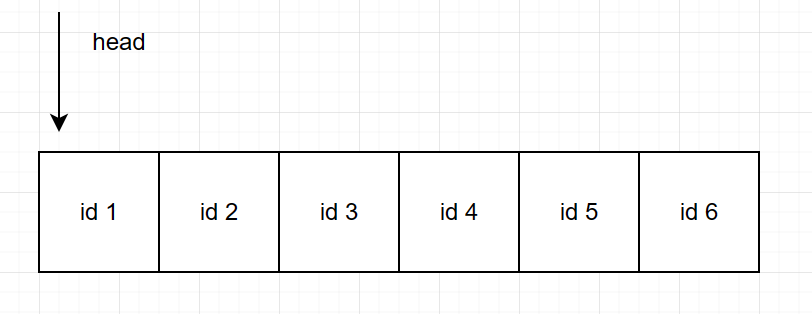
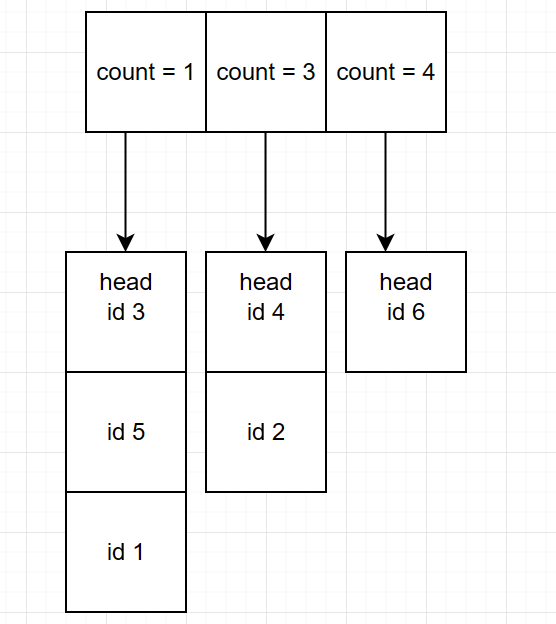
继续访问 6,7:
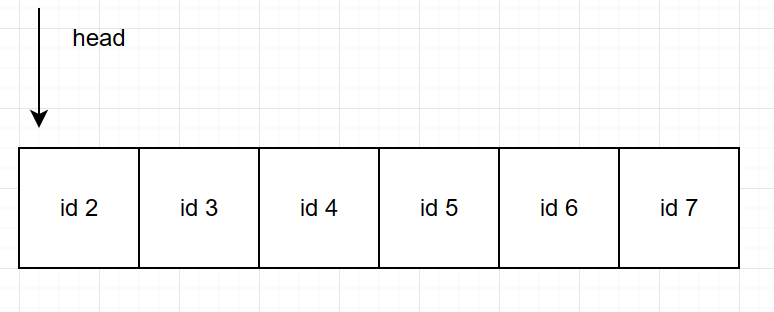
访问 7 的时候容量满了,将页面上次访问到现在时间最长的拿出来(id 1,我们按照访问顺序将它们存在了双端链表中,因此 head 就是要被替换的)。
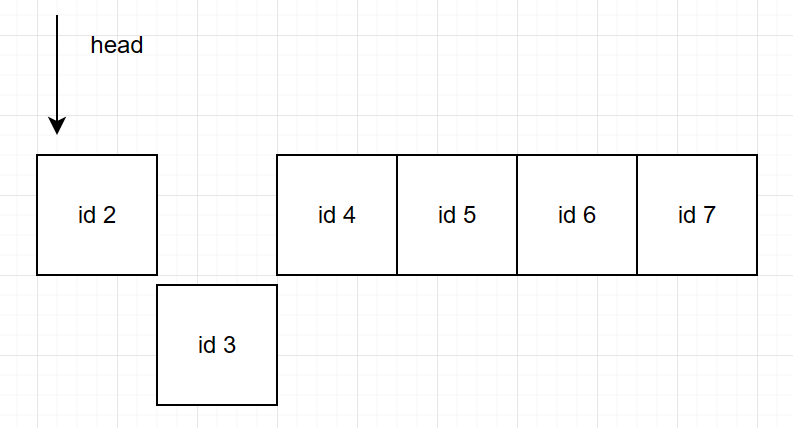
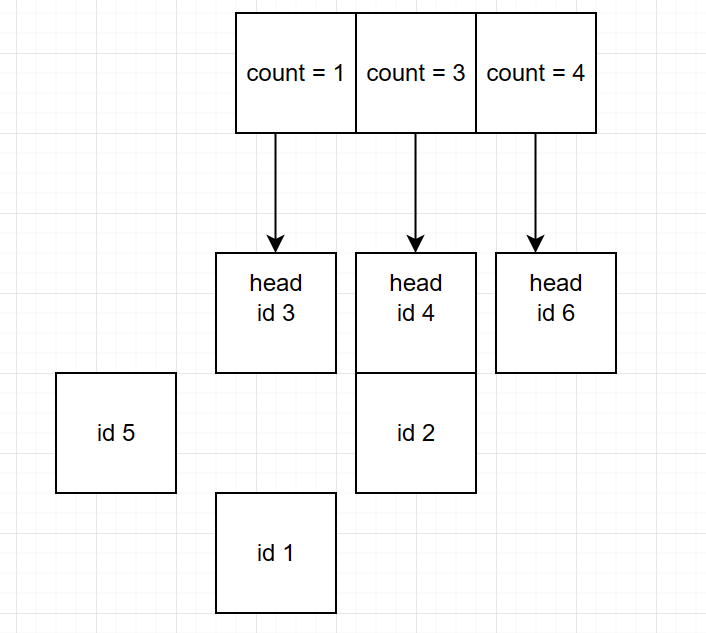
这时访问 3 会发生什么:
先取出 3 所在的节点,然后插入到列表尾部,这样双端队列就是按照上次访问到现在的时间排好序的。
取出 3 的操作就要用到哈希表将页面 id 与节点地址映射起来,这样替换操作就是一个常数的时间复杂度。
实现 146. LRU 缓存 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 class LRUCache {private :struct list_node {int key_;int value_;list_node (int key, int value, std::shared_ptr<list_node> prev = nullptr ,nullptr )prev_ (prev), next_ (next) {}int get_value () return value_; }int get_key () return key_; }class list {private :int size_;public :list ()begin_ (std::make_shared <list_node>(0 , 0 )),end_ (std::make_shared <list_node>(0 , 0 )), size_ (0 ) {std::shared_ptr<list_node> push_back (int key, int value) {lock ()->next_ =make_shared <list_node>(key, value, end_->prev_.lock (), end_);lock ()->next_;return end_->prev_.lock ();void pop_front () if (begin_->next_ == end_)return ;pop (begin_->next_);void pop (std::shared_ptr<list_node> del_node) lock ()->next_ = del_node->next_;std::shared_ptr<list_node> begin () { return begin_->next_; }int size () return size_; }int , std::shared_ptr<list_node>> map_{};int capacity_;public :LRUCache (int capacity) : capacity_ (capacity) {}int get (int key) if (map_.count (key) == 0 ) {return -1 ;const int value = map_[key]->get_value ();pop (map_[key]);erase (key);push_back (key, value);return value;void put (int key, int value) if (map_.count (key) != 0 ) {pop (map_[key]);erase (key);else if (capacity_ <= key_.size ()) {erase (key_.begin ()->get_key ());pop_front ();push_back (key, value);
LRU-K
The LRU-K algorithm evicts a frame whose backward k-distance is maximum of all frames in the replacer. Backward k-distance is computed as the difference in time between current timestamp and the timestamp of kth previous access. A frame with less than k historical accesses is given +inf as its backward k-distance. When multipe frames have +inf backward k-distance, the replacer evicts the frame with the earliest timestamp.
实现思路
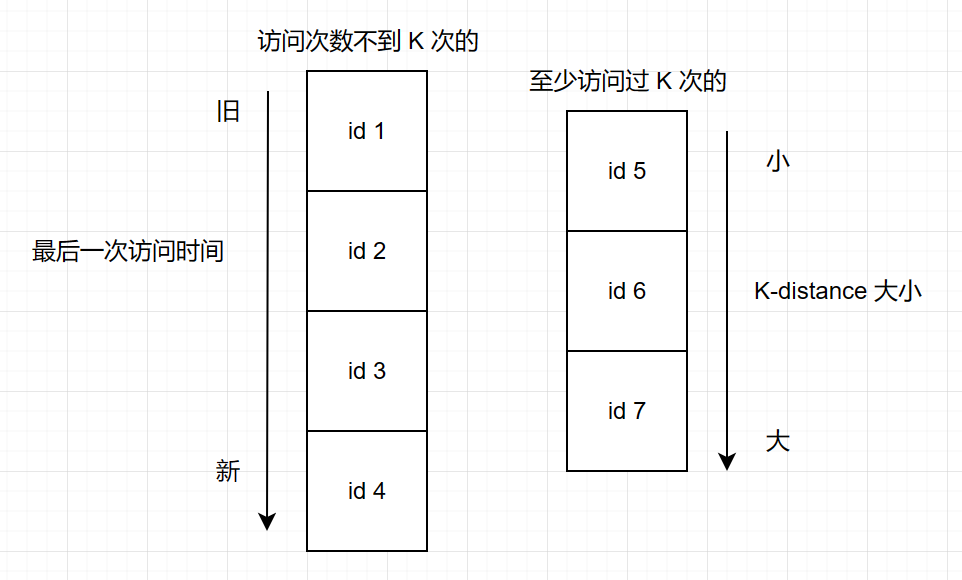
LRU-K 同时存在两种缓存:
访问次数不到 K 次,替换时被优先替换
访问了至少 K 次, 替换时,没有第一种时,才会被替换
K-distance :
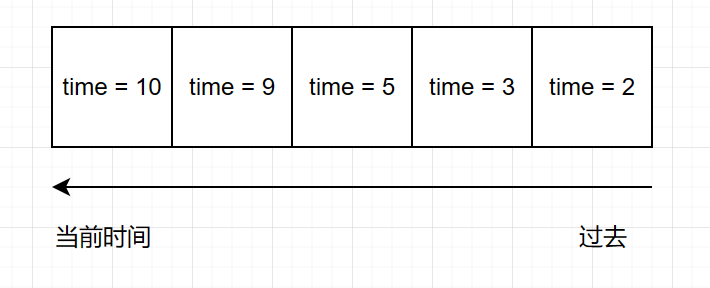
下图为一个页面的访问记录:
当 K = 2, 这个页面的 K-distance = 9
当 K = 4, 这个页面的 K-distance = 3
当 K = 6, 这个页面的 K-distance = $\inf$
第二种缓存的替换是依赖 K-distance 的,每次把 K-distance 小的替换出去(访问时间更久的)。
显然,LRU 是 LRU-1。
第二种缓存是要排序的,因此没法 O(1) 实现,不能保证新的一次访问会让一个页面的 K-distance 是最大的,可能需要插入的缓存中间。
CMU15-445 中第一种缓存的替换策略为替换第一次访问时间距今最久的页面(FIFO), 也可已使用最后一次访问时间距今来判断(LRU)。
实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 class LRUKReplacer {struct Page {int , int > value_;int count_;int > history_;Page (int key, int value, int count = 1 )value_ (key, value), count_ (count) {}bool is_k () const return count_ <= 0 ; }void record (int time) if (is_k ())pop_front ();push_back (time);if (!is_k ())int k_distance () const return history_.front ();private :int capacity_;int k_;int cur_time_{0 };int , std::list<Page>::iterator> k_map_;int , std::list<Page>::iterator> inf_map_; public :LRUKReplacer (int capacity, int k) : capacity_ (capacity), k_ (k) {}int free_size () return capacity_ - (k_map_.size () + inf_map_.size ()); }void evict () if (inf_map_.size () != 0 ) {erase (inf_que_.front ().value_.first);pop_front ();return ;erase (k_que_.front ().value_.first);pop_front ();int get (int key) if (k_map_.contains (key)) {auto [_, value] = k_map_[key]->value_;return put (key, value);if (inf_map_.contains (key)) {auto [_, value] = inf_map_[key]->value_;return put (key, value);return -1 ;void put_k (const Page &page) auto [key, value] = page.value_;auto pos = std::upper_bound (k_que_.begin (), k_que_.end (), page,const Page &p1, const Page &p2) {return p1.k_distance () < p2.k_distance ();if (free_size () == 0 )evict ();insert (pos, page);void put_inf (const Page &page) auto [key, value] = page.value_;if (free_size () == 0 )evict ();insert (inf_que_.end (), page);int put (int key, int value) if (k_map_.contains (key)) {auto page = *k_map_[key];erase (k_map_[key]);erase (key);record (cur_time_++);put_k (page);return value;if (inf_map_.contains (key)) {auto iter = inf_map_[key];record (cur_time_++);if (iter->is_k ()) {auto page = *iter;erase (iter);erase (key);put_k (page);return value;record (cur_time_++);if (page.is_k ()) put_k (page);else put_inf (page);return value;
LFU
LFU(least frequently used (LFU) page-replacement algorithm)。即最不经常使用页置换算法,要求在页置换时置换引用计数最小的页,因为经常使用的页应该有一个较大的引用次数。但是有些页在开始时使用次数很多,但以后就不再使用,这类页将会长时间留在内存中,因此可以将引用计数寄存器定时右移一位,形成指数衰减的平均使用次数。
实现思路 每次要替换时,都替换使用次数最少的,如果此时相同,就替换使用最少并且上次使用时间到现在时间最长的。当有多个使用次数相同时,与 LRU 算法一样了。
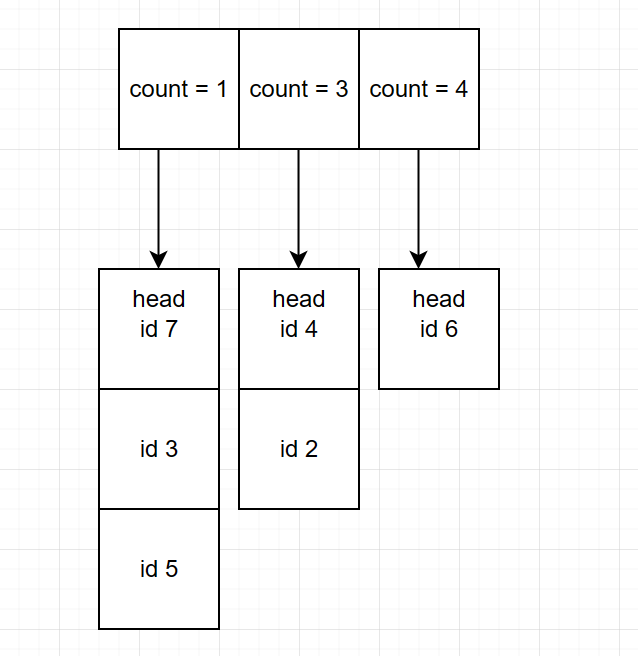
容量为 6,按照 4,7,2,4,6,6,6,4,2,3,2,5,6 的顺序访问:
把 计数 与 双端链表映射起来,记录了对应的计数的同时,又能找到上次使用时间的大小关系。
此时访问 1 :
最少使用的次数为 1,但是有 3 个页都是使用了 1 次,这时使用类似 LRU 的思想对着三个页进行判断,7 的上次访问时间到现在是最久的,替换掉 7。
访问 5 时:
这次访问需要 5 所在节点的指针来帮助移动这个节点,通用可以使用哈希映射的方式来实现。
到此为止,已经使用了两个哈希标了:
count => list
id => list_ptr
还有一个问题,怎么找使用最少的次数,哈希表是不具有排序功能的,因此需要额外的帮助来实现。
可以通过一个变量 n 来记录,当访问一个新的页面时,这个变量为 1 (新的页面 count = 1)。 当 n 映射的列表为空时,要把 n++(最小计数是 +1 的方式增加的)。
实现 460. LFU 缓存 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 class LFUCache {struct node {int key_;int value_;int cnt_;node (int key, int value, int cnt) : key_ (key), value_ (value), cnt_ (cnt) {}using list_ptr = std::unique_ptr<std::list<node>>;using list_iter = std::list<node>::iterator;private :int , list_ptr> count_;int , list_iter> key_value_;int lfu_cnt_;int capacity_;public :LFUCache (int capacity) : lfu_cnt_ (0 ), capacity_ (capacity) {}int get (int key) if (key_value_.count (key) == 0 || capacity_ == 0 ) {return -1 ;put (key, key_value_[key]->value_);return key_value_[key]->value_;void erase (int count, list_iter iter) assert (count_.count (count) != 0 );erase (iter);if (count_[count]->size () == 0 ) {erase (count);if (count == lfu_cnt_)1 ;void insert (int count, node value) if (count_.count (count) == 0 ) {push_back (value);void put (int key, int value) int count = 1 ;if (key_value_.count (key) != 0 ) {1 ;erase (count - 1 , key_value_[key]);else if (key_value_.size () >= capacity_) {erase (count_[lfu_cnt_]->begin ()->key_);erase (lfu_cnt_, count_[lfu_cnt_]->begin ());if (key_value_.count (key) == 0 )1 ;insert (count, node{key, value, count});end ());
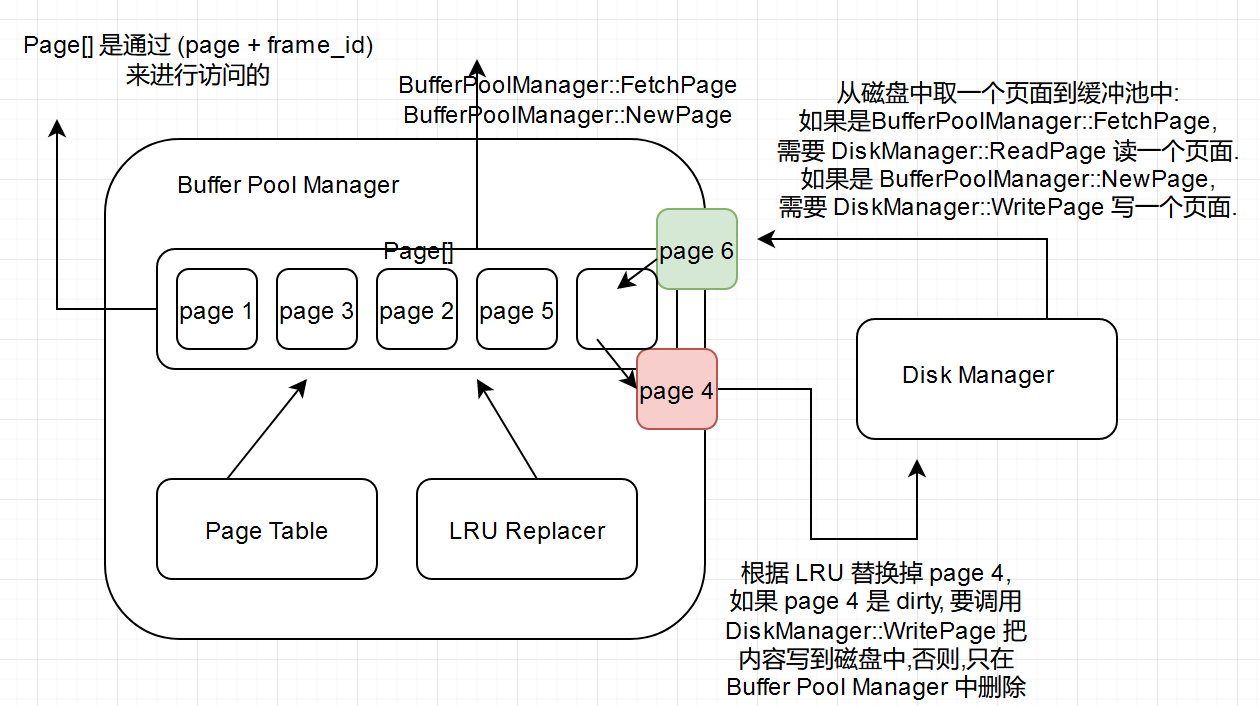
缓冲池
Page *pages 存放页面的数组
std::unordered_map<page_id_t, frame_id_t> page_table 将页面 id 与页面在数组中的位置映射起来.
std::list<frame_id_t> free_list 数组中还没有页面的下标.
通过 pages + frame_id_t 的方式来访问 page.
page_table 存储 page_id_t 与 frame_id_t 的映射来帮助 LRU 管理页面替换.
当要获取的页面在内存中, 通过 DiskManager 读上来, 使用 BufferPoolManager::NewPage 和 替换/刷新页面操作时(要判断是否时 dirty), 要使用 DiskManager::WritePage 将内容写到磁盘.
pages 中被替换出来的页面下标是无序的, 因此通过 free_list 来记录, 有页面从缓冲池中被驱逐, 就把它的下标放到 free_list 中. 当需要向 pages 中放入页面时, 从 free_list 中取出下标即可.
DiskManager 是通过 fstream 来读写磁盘的.
LRU 的小优化 使用哈希映射的方法导致, 在频繁的插入和删除操作中带来了性能损失.
使用哈希是为了起到快速查询的作用, 同样具有 $O(1)$ 的时数组, 通常不选用数组是因为 key 的类型不为数字, 这里的 key 为数字表示, 可以尝试使用数组来优化.
使用 std::vector<std::list<frame_id_t>::iterator> 来做优化, 删除时只需要赋值为 list<frame_id_t>::end 即可. 这样只有赋值的开销了.
剩下的优化应该在锁上了.
参考资料 The LRU-K page replacement algorithm for database disk buffering - acm